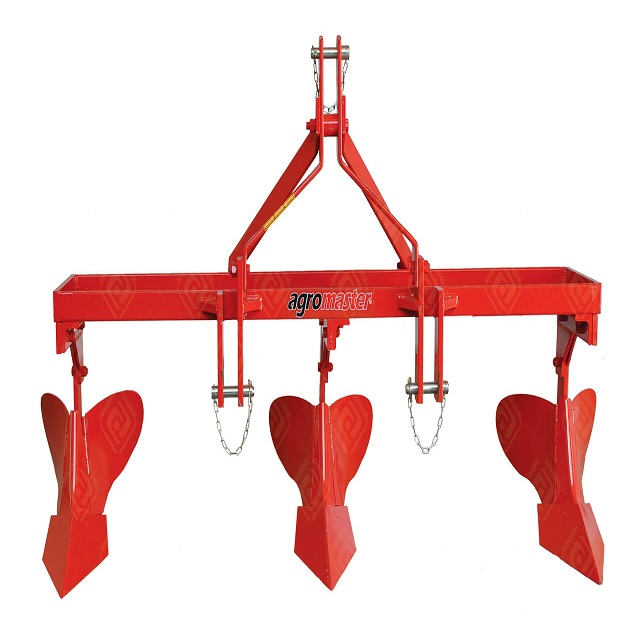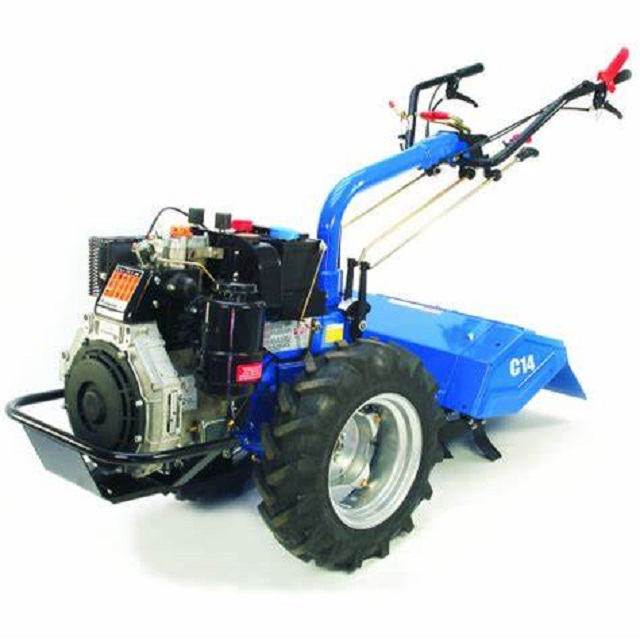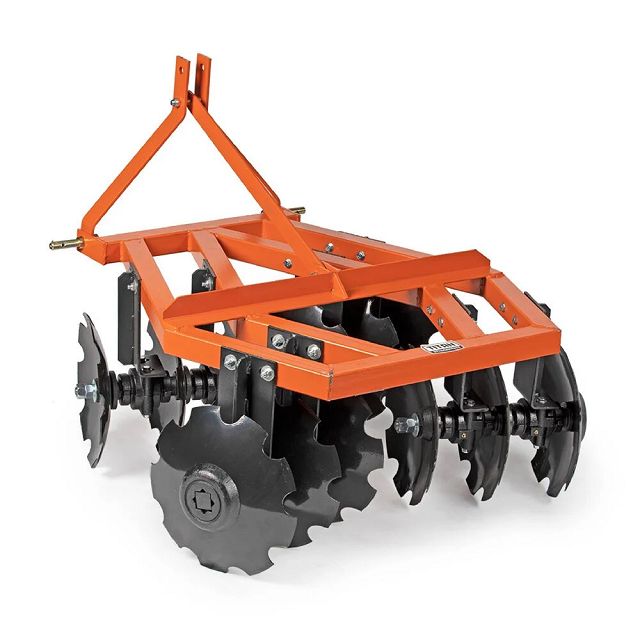
No review given yet!
 Free shipping on all orders over UGX 1 Millon
Free shipping on all orders over UGX 1 Millon
 Safe & Secure Online Payment Solutions or cash on Delivery
Safe & Secure Online Payment Solutions or cash on Delivery
 7 Days Return Policy
7 Days Return Policy
 Authentic Products with MONEY BACK GUARANTEE 100% money back guarantee
Authentic Products with MONEY BACK GUARANTEE 100% money back guarantee




